
I am sharing some of my class notes and reviewers to help test-takers of the Librarians Licensure Examination in the Philippines. This page includes the role of indexing and abstracting in information retrieval and searching.
Information retrieval - term for the processes and procedures of searching documents, images, data, and personal information from information stores such as a library, database, or the internet. It usually refers to data, documents, text, and images.
Information retrieval is a process and a system is the mechanism or way to carry out the process. An information retrieval system is capable of storing, retrieving, and maintaining information.
Database: A large, regularly updated file of digitized information (bibliographic records, abstracts, full-text documents, directory entries, images, statistics, etc.) related to a specific subject or field, consisting of records of uniform format organized for ease and speed of search and retrieval and managed with the aid of database management system (DBMS) software. Content is created by the database producer (for example, the American Psychological Association), which usually publishes a print version (Psychological Abstracts) and leases the content to one or more database vendors (EBSCO, OCLC, etc.) that provide electronic access to the data after it has been converted to machine-readable form (PsycINFO), usually on CD-ROM or online via the Internet, using proprietary search software.
Most databases used in libraries are catalogs, periodical indexes, abstracting services, and full-text reference resources leased annually under licensing agreements that limit access to registered borrowers and library staff. (Source: Online Dictionary of Library and Information Science).
Data bases have two categories:
- Bibliographic. Collection of bibliographic records to the published literature that provides access to the literature through citations or abstracts
- Non-bibliographic. Cover a wide range of other databases - stores of facts, figures, graphics, full text journals and books, images, etc. Data may be numeric or representational.
Full text database contains the complete text of each document rather than just a reference or an abstract. Full-text searching means that every word in a text is an index term.
Information Retrieval System
- Information retrieval system is a mechanism for carrying out the functions of information retrieval process.
- Organization of information may take in different forms (manual, by the use of computer or a combination of both).
- Most challenging problem: providing for the nearest possible response or coincidence
- Modern information retrieval systems: data retrieval, reference retrieval and text retrieval.
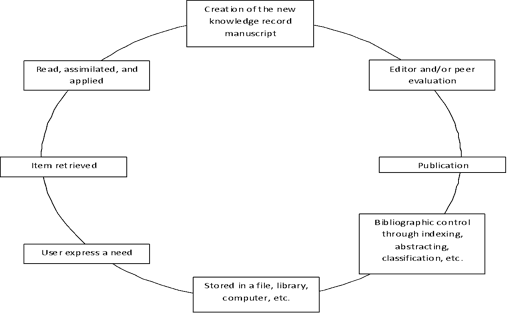
Functions involved in Searching for Information:
- The information is created and acquired for the system.
- Knowledge records are analyzed and tagged by set of index terms.
- The knowledge records are stored physically and index terms are stored into a structured file.
- The user’s query is tagged with sets of index terms and then is matched against tagged records.
- Matched documents are retrieved for review.
- Feedback may lead to several reiterations of the search.
Purposes and Uses of Indexes
- Saves time and effort in finding information.
- Identify potentially relevant information in the document or collection being indexed.
- Analyze concepts treated in a document to produce appropriate index headings based on the indexing language assigned.
- Indicate relationships among terms.
- Group together related topics.
- Direct the users seeking information under terms not chosen as index headings to headings that have been chosen.
- Suggest related topics.
- Tool for current awareness services.
- Information may be structured by evolving complexity:
- Symbols are the beginning of formalized communication.
- Words and numbers are symbols combined to convey meaning at a higher level.
- Data express discrete occurrences.
- Information is the result of processing data and giving meaning to it.
- Knowledge is the result of the information being absorbed and causing some change.
- Wisdom results in proper decisions being made with the newly formed knowledge.
- Technical
- Semantics
- Influential (effectiveness)







0 Comments